
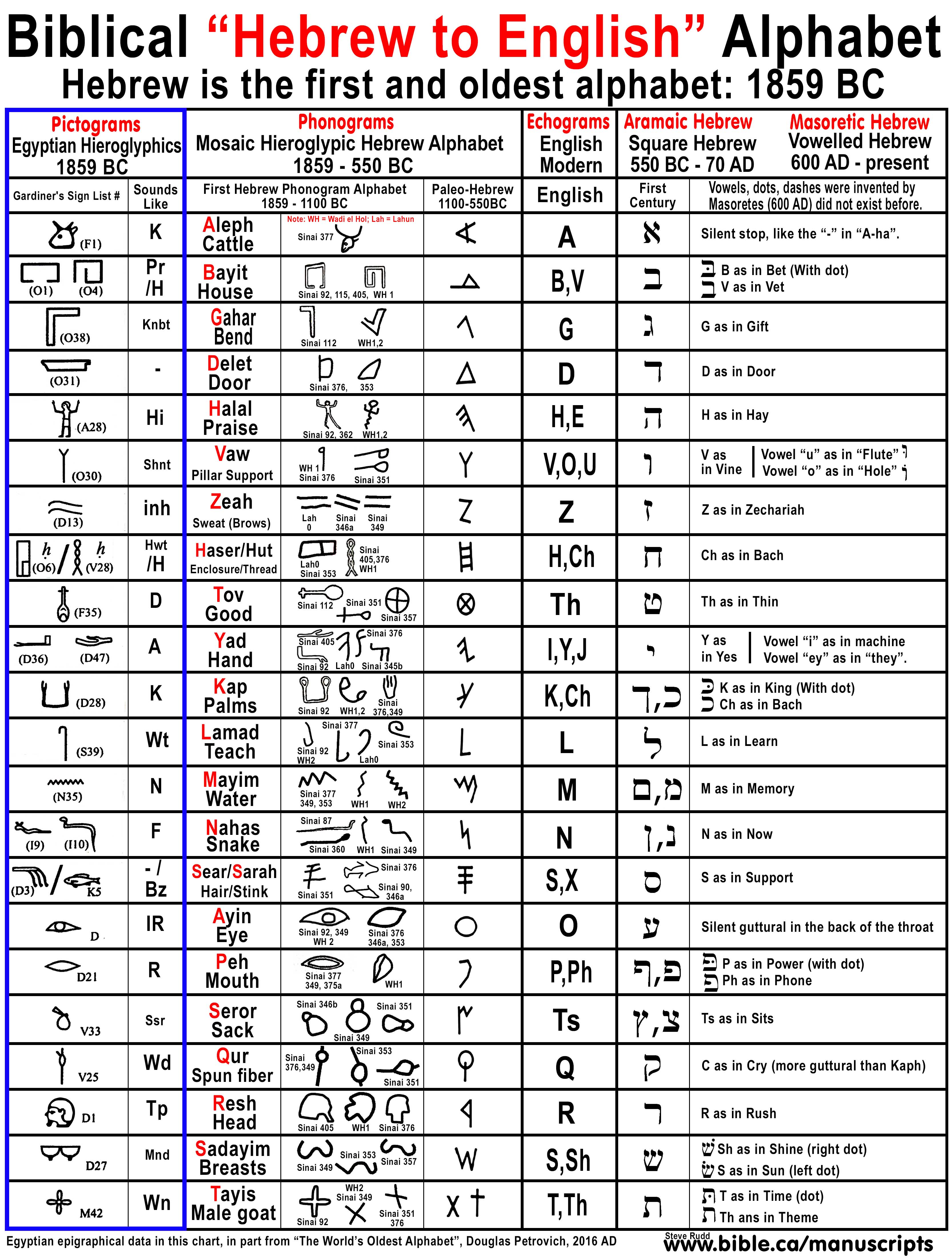

Some believed that Hebrew was the language of the angels, while the ancient rabbis maintained that Hebrew was the language originally spoken by Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden. Since Hebrew was primarily used for sacred texts prior to its revival as a spoken language, it was often called “lashon ha-kodesh,” which means “the holy language” in Hebrew. Parts of the Hebrew Bible are written in Hebrew as is the Mishnah, which is Judaism’s written record of the Oral Torah. During the Second Temple Period Hebrew was most likely used only for liturgical purposes. Once Jews were exiled Hebrew began to disappear as a spoken language, though it was still preserved as a written language for Jewish prayers and holy texts. The language was likely a commonly spoken until the fall of Jerusalem in 587 B.C.E. and evidence suggests that the Israelite tribes who invaded Canaan spoke Hebrew. The earliest Hebrew texts date from the second millennium B.C.E.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
